How large can an earthquake grow? Effect of geometrical and energetical barriers.
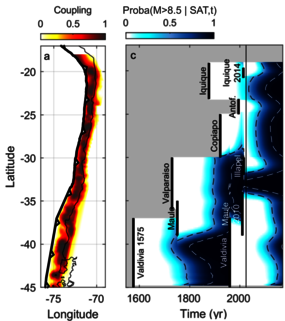
For large earthquakes to occur, seismic ruptures need to propagate long distances along-strike and overcome different types of barriers. Understanding how far an earthquake can propagate includes assessing the effectiveness of these barriers in stopping earthquakes, which depends on the characteristics of both the rupture and barriers. It also includes the evaluation of a portion of a fault to be ready to host an earthquake as it will depend, among other factors, on the energy accumulated since the occurrence of the previous large event. There is thus a time dependency.
In this talk, I will focus on both of these aspects. First, I will discuss about geometrical barriers, due to geometrical complexities along a fault (e.g. gaps and steps), within the framework of the rate-and-state friction law. Next, I will discuss about energetical barriers based on a recent extension of Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics theory to elongated ruptures. The work presented here adopts a probabilistic approach and aims to integrate certain aspects of the physics of rupture propagation into seismic hazard analysis.
Sylvain Michel, Geoazur
19
June 2025
13h
14h
Salle du Conseil